First time home buyers have traditionally faced a variety of obstacles including the high cost of housing, stagnant wages, and the difficulty involved in saving for a down payment.
If that wasn’t bad enough, recent changes by the Federal Housing Administration (FHA) now raise another potential barrier to home ownership due to the manner in which student loan debt must be evaluated.
For a variety of reasons many potential home buyers with a large load of student debt are able to obtain payment deferments of various durations. Since there was no formal payment due under the payment deferments, some of which can last for years, the FHA had for the most part simply ignored the looming certainty of future monthly payments. By not factoring in an estimated loan payment for deferred student loans, borrowers were able to lower their debt ratios for purposes of loan eligibility.
With the new FHA requirement to account for future payments on deferred student loans, many applicants may wind up with a back end debt ratio in excess of the 43 per cent currently allowed under FHA regulations. Potential home buyers who were close to the maximum for monthly debt payments may now find themselves ineligible for any type of mortgage loan.
Are the new FHA regulations fair to first time home buyers?
One could make the argument that the new rules make sense since at some point the borrower is going to be required to start making payments on the student loan debt and if the payment is large enough it could cause enough financial stress to put the borrower at risk of defaulting on the mortgage. According to a HUD spokesman, “Will that borrower actually be able to afford their loan and the student loan payment? It’s a legitimate issue to consider. Deferred student debt is debt all the same and really must be considered when determining a borrower’s ability to sustain both student debt payments and a mortgage long term. Our primary interest is to make certain that a first-time home buyer is put on a path of sustainable home ownership rather than being placed into a financial situation they can no longer tolerate once their student debt deferment expires.”
It’s difficult to dispute the logic of HUD’s position but it seems to fail to take into account the prospect of a borrower’s future income increasing enough to compensate for the additional student debt payment.
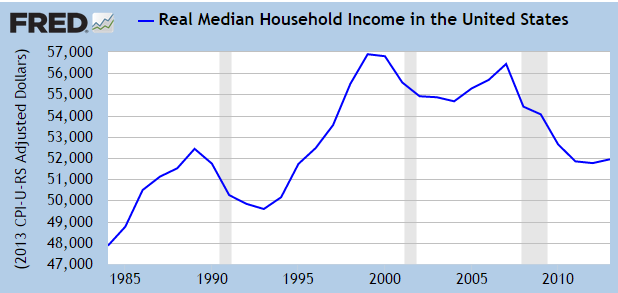
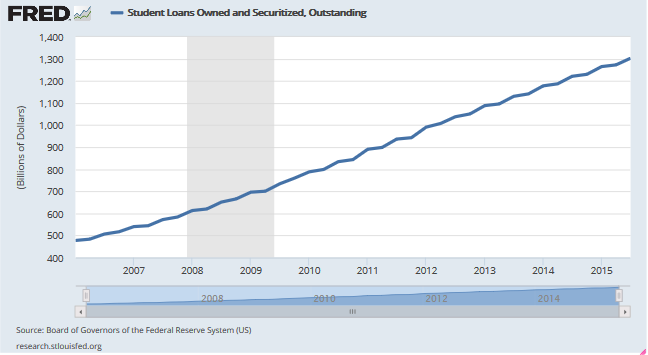
The problem with considering future income, however, is that incomes have been increasing at a very slow pace in the post financial crisis period. The prospects of higher incomes for the average worker remains speculative while the certainty of having to make payments on a student loan at some point are not. Nonetheless, the increase in the amount of student loans being handed out have been increasing at a staggering rate as students furiously borrow on the dubious prospect of obtaining a job after college that pays enough to buy a house and car, raise a family, and payoff student loans.
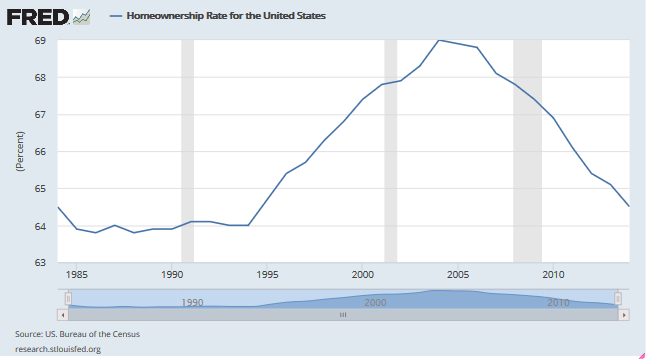
Those expecting an increase in the rate of home ownership are likely to be disappointed as more and more young people remain at home with their parents unable to take on the financial responsibilities of home ownership.
The excessively easy lending of a decade ago temporarily raised the rate of home ownership as totally unqualified borrowers bought houses on the theory that home values could only continue to skyrocket. The subsequent default of these weak and unqualified borrowers resulted in millions of foreclosures which burst the housing and mortgage lending bubble which resulted in the rate of home ownership falling right back to the long term historical average of about 65 per cent.