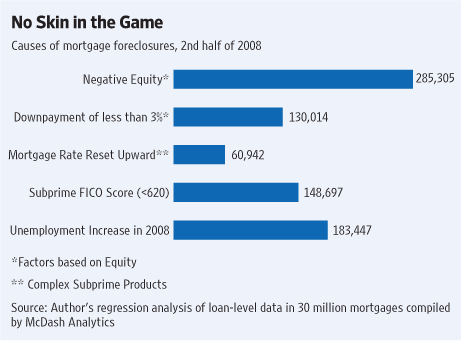
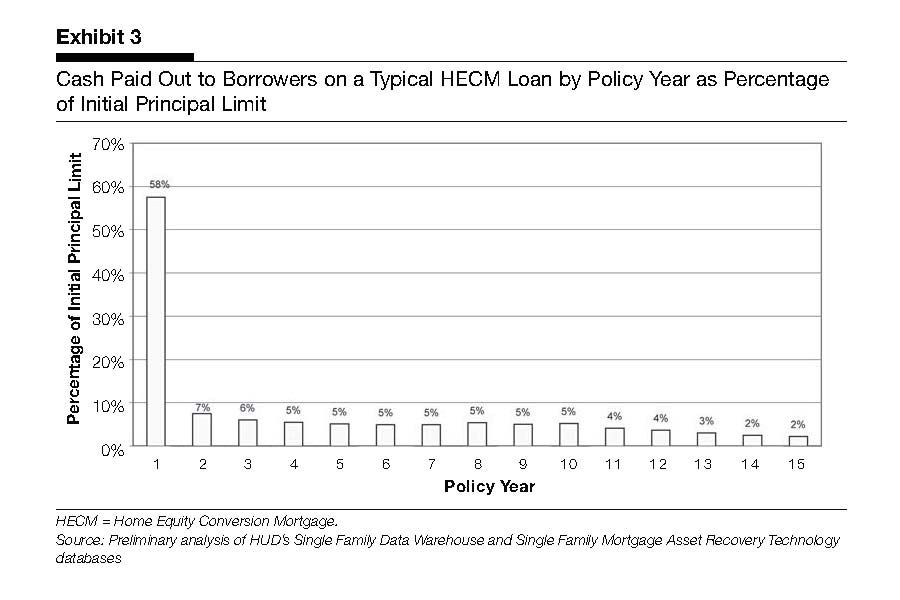
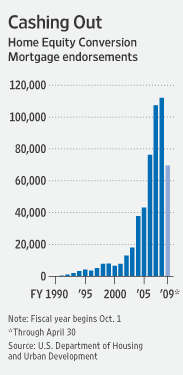
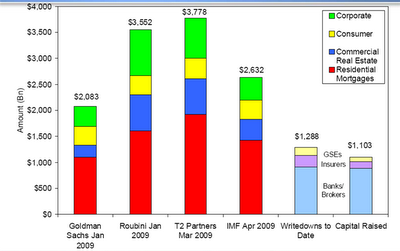
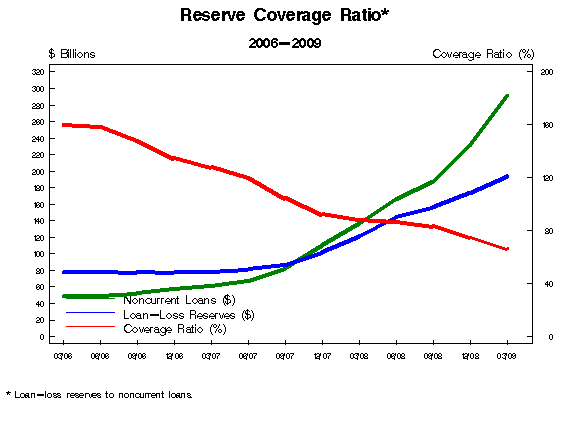
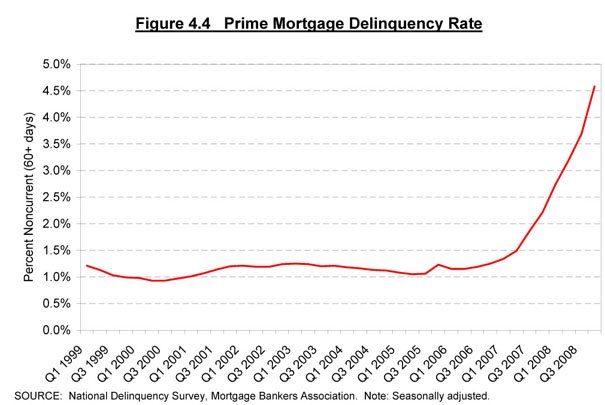
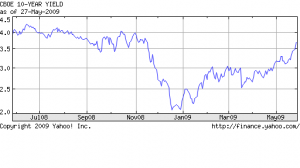
Refinances Decline as Rates Stabilize
The latest weekly survey from the Mortgage Bankers Association showed a decrease of 6.3% in mortgage loan applications. Application volume compared to the previous year increased by 16%.
The interesting aspect of the latest weekly numbers is the decline of 10.9% in the number of mortgage refinances. The percentage of refinances to total mortgage applications declined by 2.9% to 53% of total mortgage applications. With rates hovering at close to all time lows, reduced refinance activity seems to indicate that most borrowers have already taken advantage of the current low mortgage rates.
Have Mortgage Rates Bottomed?
The perfect mortgage borrower can still obtain a rate of around 5% on a thirty year fixed rate mortgage. In addition, borrowers have had numerous opportunities over the past four years to refinance in the high 4’s or low 5% range. Unless a borrower is applying for a cash out refinance, there would be little benefit to refinance a mortgage today with a rate of 5.5% or less.
If mortgage rates remain in the low 5% range, expect to see continued declines in the refinance sector of the mortgage market. In January of this year, the amount of refinances hit a peak of 85% of total mortgage applications as borrowers rushed to take advantage of low rates .
Since it is usually not worth the time and cost of refinancing unless the mortgage rate can be lowered by at least a point, I would not expect to see another mortgage refinance boom unless mortgage rates decline to the low 4% range. Considering the recent Federal Reserve report which indicates a slower pace of economic decline and an unchanged Fed monetary policy, mortgage rates may have bottomed at this point.