Investors trying to eke out a small return on their savings are finding out that buying mortgage-backed securities (MBS) can yield big losses when rates increase. It is doubtful that most investors in MBS appreciated the risk involved in buying long duration assets, regardless of the collateral behind it.
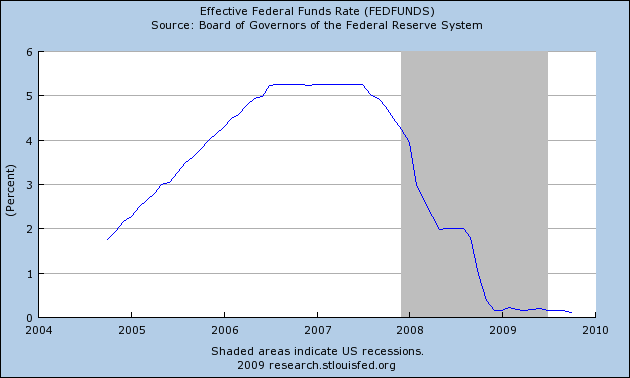
The zero-rate policy of the Federal Reserve has resulted in yield hunt by conservative investors looking for a yield higher than the near zero rates offered by banks and money market funds.
Investors buying MBS were probably seduced by the fact that they are guaranteed by various U.S. government agencies such as Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac and Ginnie Mae. The government agencies guarantee payment of interest and principal but unfortunately, the value of MBS can and will fluctuate in value depending on changes in interest rates. For example, a popular Vanguard MBS ETF has an average duration of almost 6 years. Duration measures interest rate risk and in this case, a 1% increase in interest rates with result in a 6% decline in the value of the ETF.
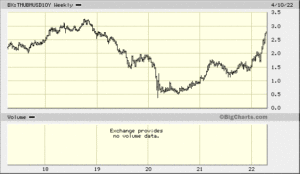
A MBS ETF as part of a laddered bond portfolio makes sense but could turn out to be a disaster if increase rates continue to increase, especially if the investor has to liquidate a position. Since the high reached in August 2021, the Vanguard MBS ETF has decline in value by over 10%, a really big loss for someone who thought they were investing in a relatively safe security. With the ETF currently paying a yield of 1.83% if would take almost six years to recoup losses if interest rates remain stable.
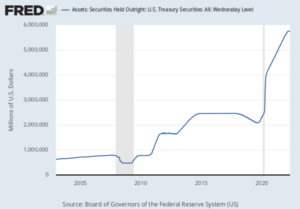
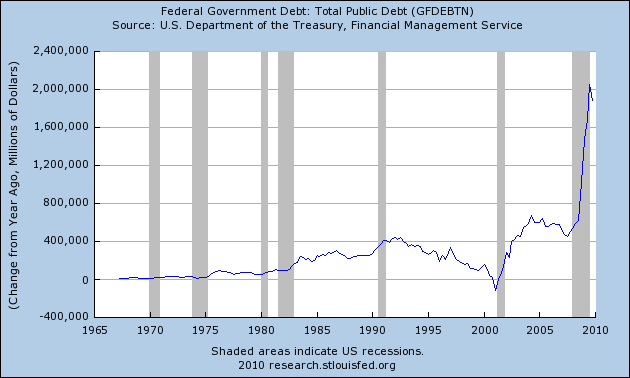
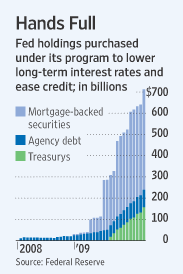
The biggest loser of all in the MBS market may turn out to be the U.S. taxpayer since the Federal Reserve currently holds almost $2 trillion of mortgage-backed assets. The Fed has been furiously purchasing MBS in an effort to keep interest rates low in the mortgage market.
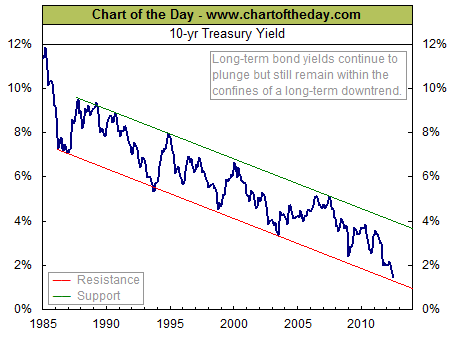
With inflation continuing to accelerate, MBS along with other long dated debt securities will continue to drop in value.