The Federal Reserve has forced long term interest rates to historic lows in a desperate attempt to “stimulate” both the housing market and the economy in general. The results have been mixed but the benefits of lower rates to borrowers are undeniable. Lower rates reduce the cost of large debt burdens carried by many Americans and increases the spending power of those able to refinance.
Exactly how much lower the Fed intends to repress mortgage rates is anyone’s guess but as interest continue to decline, the overall benefits diminish. Here’s three reasons why the Fed may wind up discovering that the economic benefits of further rate cuts will be muted at best, self defeating at worst.
1. Lower rates are becoming a zero sum game for the economy as lower rates for borrowers translates into lower income for savers. Every loan is also an asset of someone else and lower interest rates have merely been a mechanism for transferring wealth from savers to debtors. Every retiree who prudently saved with the expectation of receiving interest income on their savings have been brutalized by the Fed’s financial repression. Even more infuriating to some savers is the fact that many debtors who took on irresponsible amounts of debt are now actually profiting from various government programs (see Foreclosure Settlement Q&A – A Victory For The Irresponsible).
A significant number of retirees that I know have been forced to drastically curtail their spending in order to make ends meet while others have been forced to draw down their savings. The increased spending power of borrowers has been negated by the reduced spending power of savers. This fact seems to elude Professor Bernanke who hasn’t been able to figure out why lower rates have not ignited the economy.
2. Many consumer who would like to incur more debt are often turned down by the banks since their debt levels are already too high. Those who can borrow often times chose to deleverage instead, considering the fragile state of the economy. Anyone saving for a future financial goal (college tuition, home down payment, retirement, etc) is forced to reduce consumption and increase savings due to near zero interest rates. The Federal Reserve has destroyed Americans most powerful wealth building technique – the power of compound interest. A 5% yield on savings will double your money in about 14.4 years while a 1% yield will double your money in 72 years – and that’s before taxes and inflation.
3. As mortgage rates decline into uncharted territory, the mathematical benefit of lower rates diminishes. As can be seen in the chart below the absolute dollar amount of monthly savings as well as the percentage decrease in the monthly payment diminish as rates race to zero.
Benefits of a refinance on a $200,000 mortgage diminish as rates decline
| % Rate | Mo Payment | Mo Savings | % Reduction | Yearly Savings |
| 6.00% | $1,199.00 | |||
| 3.00% | $843.00 | $356.00 | 29.70% | $4,272.00 |
| 1.50% | $690.00 | $153.00 | 18.10% | $1,836.00 |
| 0.75% | $621.00 | $69.00 | 10.00% | $828.00 |
Closing costs at lower rates also become problematic, making it impossible to recapture fees within a reasonable period of time. With closing costs of $8,000 on a $200,000 mortgage refinance, it would take a decade to recoup closing costs.
Many astute analysts have made elaborate and compelling arguments that interest rates can only go lower. From a contrary point of view, I believe that a future rise in interest rates is a high probability event. This is the opposite of my prediction in March 2009 when I surmised that mortgage rates would decline to 3.5% – see 30 Year Fixed Rate of 3.5% Likely.
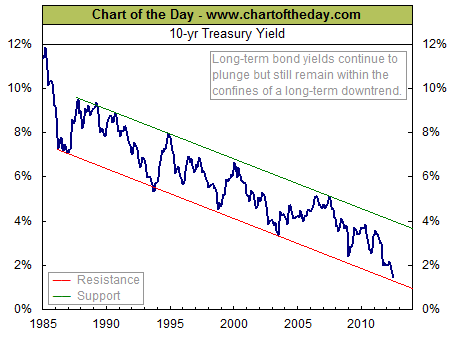
The Chart of the Day has a long term chart of the 10 year treasury and notes that the recent sharp decline in interest rates “has brought the 10-year Treasury bond yield right up against resistance of its 26-year downtrend channel.”